30 top-rated Computer Vision companies & startups
Computer Vision has already ceased to be an experiment in laboratories. Today, it is one of the working tools that helps businesses make decisions faster, optimize costs, and compete in saturated markets. From retail and logistics to healthcare, hundreds of companies worldwide are already implementing CV solutions to address specific problems, such as counting people in halls and automatic product quality control.
This article contains an overview of 30 companies and startups that actually work in the field of Computer Vision. We have chosen those who not only declare technologies, but also introduce them into business, showcase them, receive investments, and grow.
Why AI and Computer Vision are reshaping industries today
Companies are increasingly turning to AI and CV not out of curiosity, but because they cannot ignore the facts. As labor becomes more expensive, the client expects more accurate and faster service, and data becomes the main resource for growth.
Key players in retail (Walmart, Zara, Target), logistics (FedEx, DHL), manufacturing (BASF, BMW), and healthcare (Siemens Healthineers, Zebra Medical Vision) are already using CV to adapt to the market faster and keep high-quality processes.
What is Computer Vision, and how does it work in business
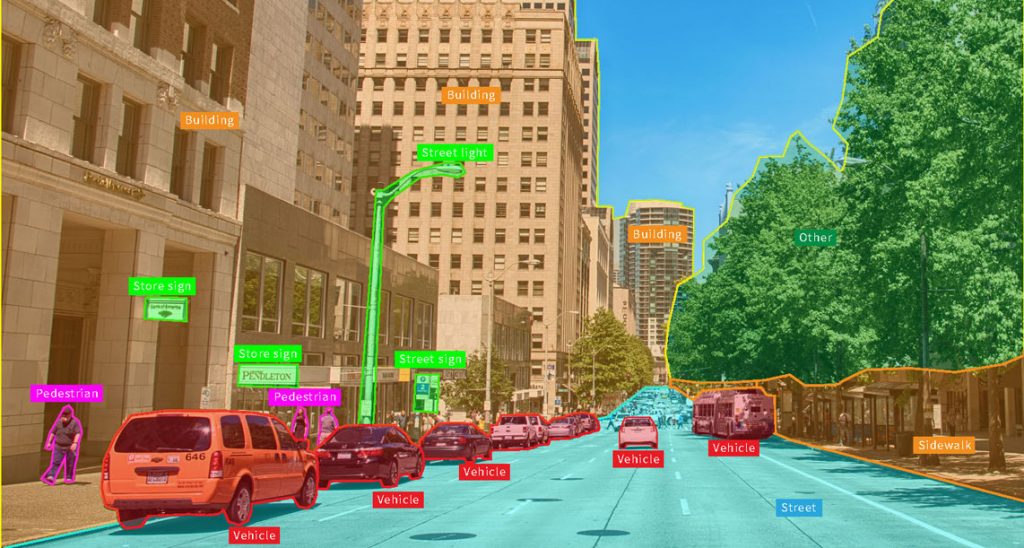
For many of you, “Computer Vision” sounds like something complex and technical. In fact, this is just a way to teach the system to “look” and “see” in the same way as a person does, but with greater speed and accuracy.
How does it work:
The image comes from the camera. This can be a video stream from a store, warehouse, production, or street. The algorithm analyzes it. It “recognizes” the necessary objects: faces, goods, packaging, car numbers, anomalies, and much more. At the output – action. The system can send a notification, count an object, fix an event, or enable an automatic process.
For example:
In retail, CV makes sure that the display on the shelves meets the standards, and the goods do not suddenly end.
In logistics, the system monitors the movement of goods and prevents losses.
In production, identifies product defects on the conveyor.
In healthcare, it helps doctors recognize pathologies in pictures faster and more accurately.
For companies that are just considering implementing such solutions, it is important to find a team that will not only write code, but also offer an application script with a clear economy. This is specialized in teams at the level of an artificial intelligence development company, which has experience in both business and engineering.
How we selected the best Computer Vision and Machine Vision companies
There are hundreds of suppliers in the computer vision market. Each has its own specialization, approach, and level of maturity. To select really strong companies, we focused not on marketing promises, but on how teams solve specific business problems. It is important not just to see the availability of technologies, but the ability to adapt them to the needs of different industries.
We used 5 key criteria by which you can judge how ready the partner is not only to implement the algorithm, but to help you achieve the result.
Experience in industry solutions
Computer vision solutions are not universal. Algorithms for retail are not suitable for healthcare. Tasks in logistics differ from those in industry. Therefore, the first criterion is the presence of experience in a specific industry: with cases, with results, with an understanding of the specifics.
The computer vision AI startups that we have included in the rating work with:
– automatic quality control of products in production;
– visual check of display and availability of goods in stores;
– recognition and sorting of objects in logistics;
– analysis of medical images;
– safety and monitoring of public spaces.
Having a narrow expertise is especially important if you are looking for a partner for image recognition software development services. Here, not only is the technical base important, but also knowledge of typical errors, risks, and business expectations.
Flexibility and adaptability to business objectives
In practice, almost no CV solution runs out of the box. Each Computer Vision company has its own infrastructure, dataset, processes, constraints, and goals. One of the key success factors is the ability of the contractor to quickly understand the business context and adapt its solution to it.
We gave preference to those teams that know how to work with the existing IT infrastructure of the customer, without requiring its complete reconstruction; offer not just an API, but a comprehensive configuration for business tasks; and can quickly scale a pilot solution after successful testing.
Full cycle from idea to implementation and support
Many developers of CV systems work only at one stage: someone deals only with the model, someone with integration. But a business must have one responsible partner who closes the entire cycle. It reduces risk, saves time, and simplifies communication.
Therefore, we have identified Machine Vision software companies that take on formulation of the task together with the business; data preparation and marking; model development and training; infrastructure configuration and integration; and real-world testing and support.
Particular attention is paid to post-launch support capabilities: how quickly the company reacts to failures, how algorithms are updated, and how scaling is accompanied.
Confirmed cases and outcome
Words are one thing, and facts are another. We looked for computer vision AI companies that have:
– cases with metrics described publicly or in a portfolio;
– customer feedback and industry references;
– grants received, investments or participation in accelerators;
– process automation, error reduction, and cost savings.
It allows you to evaluate not just promises, but the real return on implementation. Without this, any pilots remain at the level of experiments.
Reasonable value for money
Computer Vision is an investment, and here it is important to understand what you are paying for. We evaluated not only the price, but also what is included in this price: the depth of customization, the speed of implementation, the possibility of maintenance, and legal aspects (for example, issues of privacy and data storage).
A good supplier is not always the cheapest. But he knows how and how to get a return on investment, what business metrics can be improved, and when to expect the first results.
Further in the article, a list of 30 computer vision companies is provided that meet these criteria. These are both mature players with international clients and ambitious startups that have already gained market confidence. The selection is aimed at those who are looking for a reliable technological partner, and not just a development team.
How do companies achieve the data-driven decision-making process?
At Data Science UA we assist companies in extracting real value from unstructured data sources
Top Computer Vision companies in 2026
Computer vision has ceased to be a technology of “interest” and has become a working tool for retail, logistics, healthcare, and other areas. Hovewer, how to choose a contractor who will not only implement the model, but will really help the business save, speed up, or align processes?
Here is a list of top machine vision companies that have proven their effectiveness in 2024-2026. We included both technology platforms and full-cycle companies. All of them offer a real practical result, not just a technical solution. Let’s start with those we know well.
Data Science UA
Specialization: Computer Vision, AI, NLP, Data Science
Markets: USA, Europe, MENA
Format of work: development and expansion of in-house teams
Data Science UA is a computer vision company with ten years of experience in computer vision development services. It was founded in 2016 as a community and hub for AI specialists, and today it is already a mature business that combines product expertise, a strong technical team, and an understanding of business tasks.
Clients include international corporations, banks, retailers, pharmaceutical and logistics companies, as well as technology startups that need to quickly assemble or scale an AI team.
How does Data Science UA differ?
The team consists of experienced data scientists, ML engineers, architects, DevOps, and CV specialists who have completed real production projects, not just academic courses.
Before proposing a solution, Data Science UA experts analyze whether CV will really be a cost-effective tool in a particular situation. If not, they will offer an alternative. The company can connect at any stage.
If the business lacks internal resources, Data Science UA quickly forms a team of vetted specialists and takes on technical management. This is in demand among fintech, e-commerce, and B2B SaaS. The company developed CV solutions for automatic checking of the availability of goods on the shelves, customer tracking systems in offline stores, visual quality control in production, smart cameras for logistics, and automated document recognition systems.
Orbital Insight
Specialization: analysis of satellite and drone images
Market: Government, Finance, Urban
Model: SaaS platform for visual analysis of territories
Orbital Insight uses computer vision for large-scale analytics: monitoring cities, traffic, construction, and risk assessments. Their systems process images from different sources – from satellites to cameras in transport – and turn them into maps and reports. Companies are useful to those who work at the macro level: city administrations, large developers, and investment funds.
Streem
Specialization: B2C video communication with object recognition
Market: US, home repair, customer support, real estate
Application Integration SDK Model
Streem offers a platform that helps technical support and service professionals see what is happening with the client on the spot. The user’s phone camera scans the situation, the CV recognizes objects, and the specialist can give instructions in real time. The solution is especially in demand among insurance companies, equipment manufacturers, and companies providing on-site service.
Matterport
Specialization: 3D visualization of premises
Market: development, rental, architecture, retail
Model: a platform for creating digital double rooms
Matterport is a well-known computer vision company in the property market. The company offers tools that turn photos and videos of rooms into 3D models. It helps businesses quickly prepare objects for sale or lease, analyze traffic in stores, and visualize space changes. The solutions are based on a stable CV system trained on millions of premises.
OrCam
Specialization: recognition to help people with visual and hearing impairments
Market: B2C and B2G, Healthcare, Education
Model: portable devices with CV on board
OrCam is one of the most striking examples of how CV helps people directly, not businesses. The company’s devices recognize text, faces, objects, and voice them. This is indispensable for people with vision loss. OrCam works with government programs, hospitals, and also sells devices directly to users. A unique case where CV really changes everyday life.
Mech-Mind Robotics
Specialization: industrial automation with CV and 3D visualization
Market: China, Europe, Manufacturing, Logistics
Model: camera + algorithms + integration kits
Mech-Mind is one of the leaders in the segment of smart eyes for robots. Their systems allow industrial robots to “see” and make decisions. Applications – from sorting and packaging to quality control and navigation. The main plus is the complete replacement of manual labor in routine operations. Products are being actively introduced at factories in Europe and Asia.
LandingAI
Specialization: CV quality control with limited data
Market: Manufacturing, Electronics, Automotive, Food Technology
Model: CV platform with the ability to learn on small datasets
LandingAI is a project of Andrew Ung, focused on the introduction of CV in factories. The systems are suitable for companies that do not have access to large datasets. The solutions allow you to automate quality control and detection of defects in production, which is especially important for small-scale production and highly specialized lines.
Tractable
Specialization: damage assessment by photo
Market: insurance, car service, real estate
Model: AI system for processing customer images
Tractable analyzes photos after an accident or accidents and gives an automatic assessment of damage. This reduces the processing time of applications from weeks to several minutes. The company already partners with top insurers, including GEICO and Tokio Marine. The product reduces the load on call centers and speeds up work with customers.
Verkada
Specialization: video surveillance with CV functions
Market: Education, Healthcare, Office Buildings
Model: Cameras + Cloud Analytics
Verkada combines physical security and analytics. Cameras not only record video, but also recognize faces, count people, and track movements. Management – through a single cloud interface. Suitable for high-traffic areas that require quick access to analytics without additional employees.
Intel
Specialization: hardware and chips for CV
Market: Robotics, Healthcare, AR/VR, Auto Industry
Model: RealSense + neuro accelerators + chips
In addition to processors, Intel is actively developing the RealSense line – cameras with deep vision. These modules work in drones, robots, and medical devices. After buying Movidius, the company also makes energy-efficient chips for AI applications. This makes it easier to run CV systems even on devices with limited resources.
Standard Cognition
Specialization: automation of purchases in retail
Market: retail, supermarkets, convenience stores
Model: CV observation + automatic payment
Standard Cognition is building Amazon Go counterparts – stores where there are no cashiers. Cameras monitor customer activity and automatically write off payments. The solution does not require a complete reconstruction of the outlet, which makes it attractive for large networks with existing infrastructure.
Qualcomm
Specialization: chipsets with CV support
Market: Smartphones, IoT, Wearable Electronics, Security
Model: CV algorithms right on the device
Qualcomm is incorporating CV features into its mobile and IoT chips. Recognition of objects, faces, and gestures is performed locally, without connecting to the cloud. It reduces latency and protects data. Suitable for use in smart cameras, smartphones, and AR devices.
IVISYS
Specialization: automatic visual inspection
Market: Manufacturing, Conveyor Lines
Model: Industrial CV Systems
IVISYS from Sweden produces quality control systems that are installed on production lines. They record defects, deviations from the norm. All this is without human intervention. Solutions are already working in factories in Europe, where stable operation under intense load is important.
Trigo
Specialization: shops with computer vision
Market: retail, retail chains
Model: CV-system for tracking customer activities
Trigo helps retailers automate cashier-less stores. Cameras track what goods the client takes, how he moves, and how much time he spends in the hall. The system helps to fight theft and optimize the display. Used in supermarkets in Europe.
SenseTime
Specialization: CV algorithms for mass application
Market: Security, Transportation, Finance, Education
Model: Facial Recognition and Behavior Platform
China’s SenseTime operates in dozens of industries. Their technologies are used in city video surveillance, metro, and banks. The company is known for scalable CV solutions that run in real time and support millions of users.
Nvidia
Specialization: GPU and CV platforms
Market: Automotive, Healthcare, Robotics, Industrial
Model: Jetson + CUDA + SDK for CV
Nvidia is one of the key technology providers for CV. From compact Jetson boards to powerful server GPUs. The company also provides libraries and tools for developing CV applications. These solutions speed up image processing in stand-alone systems.
Hawk-Eye Innovations
Specialization: CV in sports
Market: Sports, Broadcasting
Model: cameras + tracking + analytics
Hawk-Eye assists referees and organizers of sporting events. Cameras record the exact position of the ball, athletes, and field boundaries. The system is used in tennis, football, cricket and forms the basis of VAR technology. This reduces controversy and improves the accuracy of refereeing.
Airobotics
Specialization: autonomous drones with CV
Market: Safety, Infrastructure, Extractive Industries
Model: drone + CV + automatic station
Airobotics is building drones that can take off and operate without an operator. Cameras analyze objects on the ground, create maps, and detect changes. This is useful in mines, construction sites, and protected facilities. All control is through a single platform.
Pleora Technologies
Specialization: Components for CV Systems
Market: Medical, Logistics, Production Lines
Model: Hardware + Video Software
Pleora develops interfaces and modules for video capture and transmission that are integrated into CV solutions. Their components are used in medical equipment, logistics systems, and inspections. This is a technical “backend” for machine vision systems.
Movidius
Specialization: energy-efficient CV chips
Market: Smartphones, AR/VR, Drones
Model: CV hardware acceleration on edge devices
Movidius, a subsidiary of Intel, makes CV processing chips right on the device. This allows you to run AI applications on gadgets without the cloud and reduces energy consumption. Solutions are used in augmented reality glasses, cameras, and smart drones.
How do companies achieve the data-driven decision-making process?
At Data Science UA we assist companies in extracting real value from unstructured data sources
Top computer vision startups
Standard Cognition
Specialization: Retail Shopping Automation
Market: Retail, USA, Europe
Model: CV-system for stores without cash registers
Standard Cognition creates technologies that allow customers to shop without cashiers. Cameras track the movements of customers and the goods they take from the shelves. The system automatically calculates the cost and debits the funds. This approach reduces staff costs and helps fight queues. The technology is already being introduced in supermarket chains and small stores.
Regna
Specialization: biometrics and behavioral analysis
Market: Fintech, Safety, HR
Model: SaaS solutions for evaluating personnel and customers
Regna uses computer vision and behavioral analytics to analyze people’s facial expressions, gestures, and reactions. This is used in interviews, staff training, in the field of finance to assess the risk of the client. The company’s products are already used in banks and HR agencies in Europe and Asia.
Descartes Labs
Specialization: analysis of satellite and geodata
Market: agro, logistics, ecology, government
Model: analytical platform with CV and ML
Descartes Labs processes images from space, applying CV to monitor agriculture, pollution, and infrastructure status. The platform helps large corporations and government agencies make decisions based on real-time visual data.
Bossa Nova Robotics
Specialization: retail inventory
Market: USA, supermarkets, warehouses
Model: Robots with CVs to check shelves
Bossa Nova robots move around the store and scan shelves. They record the presence of goods, calculation errors, and price tags. It reduces manual audit costs and speeds up the response to product shortages. The company partnered with Walmart and other major chains.
Neuromation
Specialization: synthetic data and model training
Market: AI Development, Industry 4.0, Robotics
Model: generating synthetic data and training CV models
Neuromation offers solutions that help accelerate the training of computer vision models through synthetic imaging. This is especially useful where there is no access to real data, or it is difficult to collect it: medicine, production, and transport.
AnyClip
Specialization: video analytics and media content automation
Market: Media, Marketing, Content Platforms
Model: Video Content Analysis Platform
AnyClip uses CV to recognize scenes, faces, and objects in videos. This allows you to automate search, ad placement, and moderation. The company’s solutions are used on streaming platforms, news aggregators, and advertising agencies.
EyeSight
Specialization: eye and gesture tracking
Market: Automobiles, Consumer Electronics, AR
Model: CV plug-ins
EyeSight develops technologies that capture where the user is looking and what movements they are making. This is used in cars (driver monitoring), in augmented reality headsets.
Xnor AI
Specialization: CV on edge devices
Market: IoT, Cameras, Smart Devices
Model: ultra-efficient models on local devices
Xnor AI makes models that work without an internet connection. This is important for surveillance cameras, consumer electronics, and industrial sensors. The company was acquired by Apple, and its technologies formed the basis of CV functions in the brand’s new devices.
Onfido
Specialization: biometric identification
Market: Fintech, HR, Rental, Digital Services
Model: SaaS solutions for user verification
Onfido checks the identity of the client from photos and videos, comparing them with documents. This is important for banks, rental services and freelance exchanges, where you need safe and fast onboarding. Clients include Revolut, Orange, Deliveroo.
Cerence Inc
Specialization: interaction with the driver through voice and CV
Market: Automakers, Embedded
Model: AI platform for smart cars
Cerence uses CV and voice analysis to improve UX in cars. The system determines who is driving, monitors facial expressions and eye movement, and helps to adapt the interface and respond to driver fatigue. Among the partners are BMW, Mercedes, and Audi.
Key mistakes to watch out for
When a business starts working with computer vision technologies, especially as part of automation or digitalization, errors at the start can be costly. Below are the 5 most common miscalculations that we regularly see in projects of machine vision companies of various sizes.
Incompatible systems and technologies
Mistake: Starting a CV solution that is not adapted to the current IT infrastructure.
What happens: Teams implement cameras, software, or algorithms that do not integrate with internal accounting, security, or logistics systems. Everything has to be redone, time is spent, the budget is affected, and failures occur.
What to do: It is important to conduct a compatibility audit before launch. Preferably, with the involvement of the best computer vision companies. Everything is taken into account: from data transfer protocols to API compatibility and response speed to signals from equipment.
Lack of technical support and maintenance
Mistake: No support plan after system startup.
What happens: CV modules start to malfunction, the camera gets dirty, the light changes, and the algorithms go blind. No support – the system is idle.
What to do: technical support should not be nominal, but should be the prescribed part of the contract. Better – with clear SLAs and the ability to remotely configure. At the start of the project, it is worth checking if the partner has a team that is responsible for post-integration issues.

Limited scalability options
Mistake: the solution works only in the pilot, and then runs into limitations.
What happens: the CV system showed itself on the same line, but when scaled by 10, the load increased, the data did not pass, and there was no centralized control.
What to do: even when designing, lay down the possibility of scaling, both by the number of cameras and by the load on the server. Use cloud solutions or hybrid models where possible.
Weak security practices
Mistake: A CV system camera is a point of vulnerability that no one deals with.
What happens: The CV stream leaves without encryption, and access to the system can be obtained from the outside. Especially relevant in projects in production and retail.
What to do: CV is not only vision, but also data. You need to apply the same approaches as for critical IT systems: encryption, access control, and logging of actions. Plus regular security audits.
Prioritizing budget over performance
Mistake: the cheapest solution is chosen without assessing functionality.
What happens: a camera with a bad sensor does not “see” the necessary details, the algorithm does not work in your lighting conditions, data is pouring in, and errors are growing. And then everything is written off as “AI doesn’t work”.
What to do: in computer vision, price ≠ redundancy. The quality of the optics, the accuracy of the model, and the stability of the software directly affect the efficiency. It is better to start with an MVP on quality hardware than to save money and get a system that cannot be used.

AI trends 2025 – Top innovations
read MORE

Future trends in Computer Vision software companies
Computer Vision has already moved from the experimental stage to the phase of mature business solutions. Below are the key areas to watch over the next 1-2 years.
1. Moving from centralized to edge
On-site processing right on the device or camera becomes standard. This reduces the load on the network, speeds up the response, and increases the resistance of the system to failures. Top computer vision companies like Nvidia, Qualcomm, and Intel are actively promoting chips that allow you to run CV without a constant connection to the server.
2. Growing interest in synthetic data
Training CV models requires large volumes of labeled images. In reality, such datasets are difficult and expensive to assemble. Therefore, AI computer vision companies are starting to use synthetic data – visual simulations that are generated artificially, but are close to reality. This is especially true in medicine, industry, and defense.
 3. Integration of CV with other decision-making systems
3. Integration of CV with other decision-making systems
Computer Vision is increasingly becoming part of a wider architecture: CV captures data, and decisions are made based on aggregate analysis (taking into account IoT, ERP, and BI). Example: the camera records that the product is over – the signal goes to the warehouse system, an order is generated, and the manager receives a notification.
4. CV as a Service: CVaaS model propagation
Companies don’t want to deploy systems from scratch. It is easier for them to pay for a ready-made API or rent a ready-made infrastructure. CV platforms “by subscription” are already appearing – from the security of facilities to the analysis of behavior in retail. This approach speeds up startup and lowers the entry threshold.
5. Focus on the interpretability of models
Business is increasingly demanding to explain why the model made this or that decision. This is especially important in fintech, medicine, and legal proceedings. Therefore, companies will develop CV models by showing which areas of the image the system was guided by when recognizing.
FAQ
Which technologies drive modern computer vision?
Computer Vision today works at the intersection of several technologies. The main ones are:
– Neural networks and deep learning: they analyze images and “learn” to find the necessary objects on them – people, goods, parts, defects.
– GPU and specialized chips: speed up the processing of video and images in real time, allowing you to run complex models on local devices.
– IoT and edge devices: cameras and sensors with local data processing without sending to the cloud. This is important where high reaction speed is needed, or there are traffic restrictions.
– Storage and streaming systems: Provide stable operation in large volumes of video and images.
All these technologies work in conjunction. The better integrated they are, the more sustainable the system is.
Can Computer Vision tools be used with existing hardware and software?
In most cases – yes. The main thing is to assess how the current equipment and the IT environment are ready to work with CV.
There are usually three approaches:
Integration “on top” of current cameras and software: if the cameras provide the desired quality, you can add a CV module separately – for example, through the API or a local server.
Modernization of cameras while maintaining IT infrastructure: only the “eyes” of the system change, but logic, accounting, and reporting remain.
Full integration of new CV solutions: used if older systems interfere with automation or do not scale.
In any case, it is important to conduct a technical audit: evaluate the video format, interfaces, protocols, and compatibility with business systems (WMS, ERP, CRM, etc.).
What types of computer vision systems exist?
All CV systems can be roughly divided by functionality and purpose:
Classification of objects: the system determines what is shown on the frame (product, person, transport, defect, etc.).
Recognition and identification: allows you to “recognize” specific objects – faces, car numbers, QR codes.
Real-time tracking: The system monitors the movement of objects. Useful in logistics, production, and safety.
Segmentation: divides the image into semantic zones – for example, where the operator’s hand is located, and where the robot’s coverage area is.
Behavior analysis: determines how a person or object moves, interacts with space. Used in retail, healthcare, and transport.