How do AI agents examples change business?
What are AI agents, and why is everyone talking about them?
When it comes to AI, most people immediately think of chatbots like ChatGPT. However, AI-based agents are not just responsive programs.
AI agents work on the principle of getting a task, collecting data, choosing an approach, completing a task, and, if necessary, adjusting behavior based on the result. This is no longer a tool in the hands of an analyst, but an independent performer.
For example, an agent can negotiate with suppliers himself, update prices based on demand, track variances in logistics, or plan advertising campaigns. It doesn’t just “react”, it initiates action, like a real worker.
For businesses, this means less manual routine, fewer human errors, and faster decision-making. This is especially critical for companies that want to grow but face a shortage of specialists, time, or budget.
At Data Science UA, we provide AI development services, where we create agent solutions for specific business tasks – from customer interaction models to intelligent process planning.
Key features of effective AI agents
What distinguishes a “working” AI agent from just an advanced script? There are several mandatory signs:
- Goal setting.
The agent must understand what task he is solving. Conditionally – “increase revenue,” “reduce costs”, “serve the client”. This is not just an algorithm, but a system aimed at the result.
- Autonomy.
He doesn’t expect every team. He acts within the set goals, chooses the tools himself, and adapts himself to change.
- Working with context.
The agent understands what is happening around. It does not just process the request, but takes into account the user’s history, market situation, seasonality, and KPI of the company. This allows for more informed decisions.
- Training opportunity.
A good agent is a trainee. He can adapt to new information, analyze past actions, and adjust his work. This allows you not to rewrite the system every month, but simply feed it with data.
- Transparency.
Explainability is important in business. The system should make it clear why it made this or that decision. This helps managers trust the agent and, if necessary, intervene quickly.
- Integration.
The AI agent development company must work within the company’s ecosystem: CRM, ERP, BI, marketing, and support services. This is not a separate module, but part of the infrastructure.
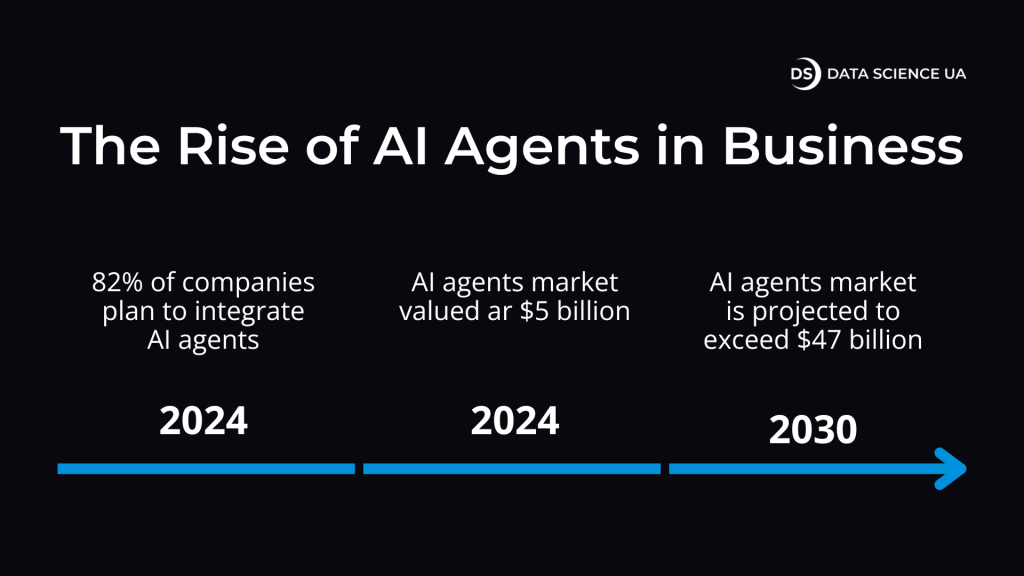
The rise of AI agents in business: from 2024 till 2030
5 types of AI agents depend on their autonomy
Unless you work directly with artificial intelligence, everything can seem complicated. In practice, most agent decisions are based on quite understandable principles. We often explain to clients: You don’t need to be a techie to implement an AI agent. It is enough to understand what types of AI agents examples are and how they work.
In this part, we will tell you which agents are used in business, how they differ, and where it is better to use which one.
Basic reflex agents
This is the simplest one in the AI agents examples. It acts on the principle of “stimulus – reaction”. That is, the agent receives input (for example, the user pressed a button on the site), matches it with predetermined conditions, and performs a specific action (for example, shows a pop-up with a discount offer).
Such agents are useful where you need a quick response to repeated events: in marketing automation, in customer support at the first touch, in online consultations, in simple actions in the warehouse.
But there’s a limitation: They don’t remember the context. They don’t care who is in front of them – a new client or a permanent one. They do not learn, do not analyze experience. Their task is to react here and now.
From a cost point of view, this is the most affordable option. But it’s important to understand that it only works in very clear scenarios. If the business process is more complex, the agent will start to make mistakes or react differently.
Model-driven reflex agents
The next stage is agents that act not just by signal, but rely on an internal environmental model. They kind of “understand” what’s going on and make a decision based on experience and context.
This is already much closer to the real work of the company. The agent not only sees that the client has entered the site, but also analyzes their behavior, past purchases, geography, device, and time of day. He can compare all this and offer a product that is really likely to interest the user.
Example:
In retail, such agents manage personalized offers. Let’s say a customer buys sneakers every three months, often returning to the X brand. The agent remembers this, and 80 days after the last purchase, he automatically offers a new model, without the participation of a marketer.
Such AI agents examples are more difficult to develop and require more data, but produce more accurate and sustainable results. Especially in an unstable environment where you need to adapt – in e-commerce, in production, in logistics, in telecoms.
Goal-oriented agents
If base agents simply respond to signals, and more advanced agents focus on the environment model, then goal-oriented agents work for a specific purpose. They have a clear task, and they are looking for a way to achieve it, even if the path is not fully spelled out in advance.
The agent does more than just execute a given reaction. He strives for the goal and makes decisions himself that bring him closer to the desired result. This is especially useful in cases where there are many options for action.
When it comes to the production of drugs, non-compliance with safety standards is not just a formality, but a risk to patient health, company reputation, and millions of dollars in contracts. One of the industry leaders turned to Data Science UA with a clear request: how to transfer hygiene control from the human eye to an algorithm that does not get tired, makes no mistakes, and does not miss important things.
The team proposed a computer vision-based solution: the system analyses the video stream from cameras in real time and automatically determines whether all employees are following the protocols. Are they wearing a mask? Are their hair and hands covered? Is the workwear in good condition? Violations are instantly notified to the responsible person in Messenger or via the dashboard.
The old cameras remained – only the software was added. The algorithm is constantly learning: the more it sees, the more accurately it works. It is adapted to different conditions: it can be used in production halls, warehouses, or laboratories. And most importantly, it is not interested in shift changes or the human factor.
After the launch of the new system, the number of sanitary control violations decreased by 40%. Not because people became perfect. But there is a permanent, objective, and impartial supervisor who does not need a coffee break.
Utility-driven agents
Sometimes one goal is not enough. You need to understand how profitable it is. This is where utility-driven agents come into play – those AI agents examples assess not only the achievability of the goal, but also its usefulness for business.
Example:
You can deliver goods to a customer in 2 hours, but it will cost the company three times more. Or it can be delivered in 24 hours at no additional cost. The agent compares the benefits and costs and offers the best option.
Unlike goal-oriented systems, utility agents work with priorities, risks, and costs. This makes it possible to take into account limited resources: budget, personnel, and production capacity.
If your company operates in conditions of frequent choice between “fast”, “cheap”, and “quality”, this type of agent architecture can be especially useful.
Adaptive learning agents
This is the next level. Such AI agents examples know how to learn, not just to act according to predetermined rules, but to improve their actions over time.
What are they doing?
- collecting data from the medium;
- analyze their past actions and results;
- Adjust behavior to act more accurately next time.
A simple example:
The support service receives hundreds of calls daily. An adaptive agent starts with basic answers, but every day it analyzes which of them lead to a positive assessment of the client, and gradually changes patterns, improving its communication style.
In industry, such agents can be trained on data from sensors and correct the operation of equipment, reducing defects. In logistics, to build more accurate forecasts of delivery, based on historical data and external factors (weather, season, traffic jams, etc.).
Adaptive agents are most valuable in areas where everything is changing: demand, customer behavior, and the external environment. Instead of constantly revising rules and strategies manually, such agents themselves adapt and continue to work even in new conditions.
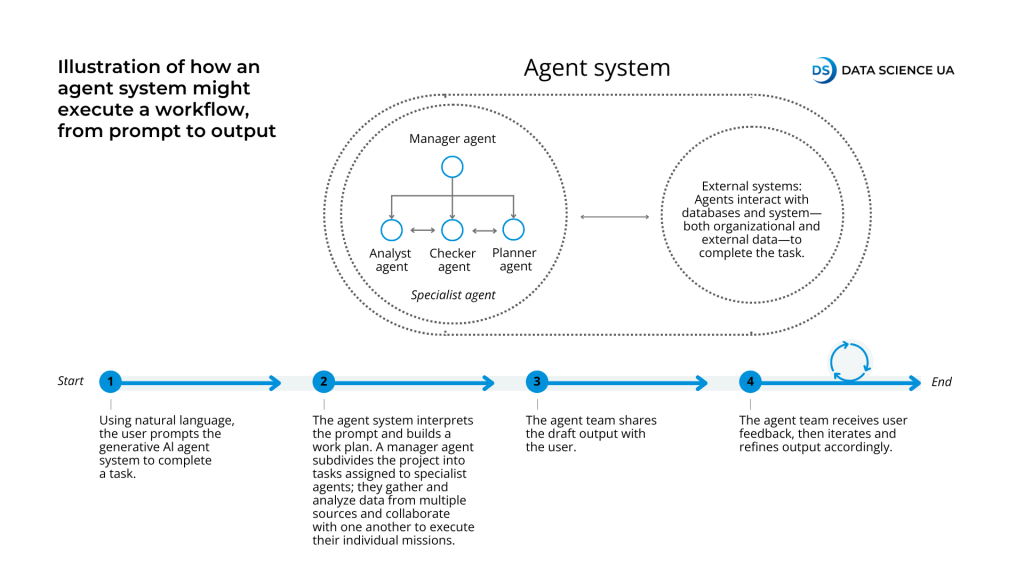
How an AI agent system might execute a workflow: from prompt to output
Benefits of using AI agents in business
The market is growing, and customer requirements are growing even faster. Companies are forced to work faster, with less cost, and with minimal errors. But there are not enough people, and the processes are becoming more complicated. It is here that AI agents provide a practical advantage: they close some of the tasks that previously required the constant participation of specialists. Below are the specific business benefits you can get now.
Improved efficiency and automation
What a person used to do: sorted applications, answered typical letters, checked documents, checked numbers, and updated tables. All this can be automated. The agent connects to the desired systems, processes incoming data, and performs script actions. Fast, without fatigue and mistakes.
For example:
- Legal entities can process contracts in minutes instead of days.
- HR commands – filter thousands of resumes according to given criteria;
- Logistics companies automatically recalculate routes depending on traffic jams or failures in warehouses.
It doesn’t mean that people should be fired. On the contrary, automation frees teams from the “little things” that take the lion’s share of the working day. People focus on difficult or creative tasks, and agents take on everything else.
If you are interested in implementation, our page with Machine Learning Services contains examples of agents and stages of implementation for business tasks.
Enhanced customer experience
Today, the client expects a quick reaction, a personal approach, and understandable solutions, regardless of the time of day and communication channel.
AI agents allow you to maintain a level of service that was previously available only to large companies with armies of operators. Examples of agents in AI:
- chatbots that do not just “talk”, but process orders, change reservations, or select goods;
- Intelligent agents examples, that analyze the client’s appeal and direct him immediately to the desired specialist, bypassing the chain of transfers;
- systems that predict when a customer might leave and offer a personal promotion in advance.
It’s not that the technology works that matters. It is important that it allows the client not to wait, repeat, and not get annoyed. As a result, there is higher loyalty, more repeat purchases, and less conflict.
Data-driven decision making
AI agents can not only act, but also prompt. They process large amounts of data and draw conclusions based on it that are difficult for a person to notice.
Types of agents in AI with examples:
- In retail, predicting which products will sell worse next week.
- In production, the identification of equipment that is most likely to fail.
- In marketing, understanding which messages work better on certain days, hours, or segments of customers.
We are not talking about “magic insights”. This is systemic work: the agent tracks changes, notices patterns, and suggests hypotheses. The leader receives not just numbers, but recommendations: where to invest, where to cut, what to redistribute.
Previously, such things required an analytical team and weekly preparation. Now, available in almost real time. Especially if data is already collected inside CRM, ERP, BI, and other systems.
Cost reduction and scalability
AI agents allow you to scale your business without proportionally increasing costs. One agent can process thousands of calls per day, perform hundreds of simultaneous actions, and support different channels (mail, chat, CRM) in parallel.
What examples of intelligent agents in AI give?
- Reduced staff and training costs;
- less dependence on fluid and human factors;
- growth readiness without overloading the current infrastructure.
This is especially felt in areas with seasonal jumps: retail, tourism, logistics, and customer support. Instead of temporary personnel, an agent is connected, which quickly scales and disconnects when the need decreases.
Top real-world examples of AI agents
Today, AI agents work next to us – on the phone, on the bank’s website, in a hospital, logistics, and online stores. The problem is not to understand what an AI agent is, but how to properly use it in a particular business.
Each of the solutions below is a working one already implemented in companies of different sizes. Not fantasies. And specific tasks that have become cheaper, faster, or easier thanks to automated agents. So, what are examples of AI agents?
Support chatbots
Customers don’t have the patience to wait in line. A good AI chatbot takes over the routine: answers frequently asked questions, helps with all the order’s stuff.
The main thing is that it works 24/7. Even at night, when the whole team is asleep, the client receives a response. And in difficult cases, the bot gently translates the dialogue to a live operator without annoying the user with unnecessary mechanics.
Banks, online stores, insurance companies, and even small online services have been using this format for a long time.
Autonomous cars and drones
Amazon warehouses and FedEx logistics already have robots moving around the warehouse, sorting loads and delivering orders. In agriculture, drones independently fly around fields, assess yields, and find pest foci.
Piloted unmanned taxis are already being tested in California and China. These are also agents: they “make decisions” in real time, analyzing the situation, pedestrians, and road signs.
AI agents in finance
Applications – from KYC and transaction validation to analyzing client behavior in the application. AI can predict the user’s outflow in advance, suggest optimal credit conditions, and automatically detect fraud.
More about it in AI in Fintech.
AI in healthcare
Here, the agent can do the work that doctors take hours to do:
- Sort patients by priority.
- Predict risks of readmission;
- Analyze medical images with higher accuracy than humans.
Thanks to this, doctors focus on critical cases, and patients get help faster.
Read case studies on AI in Healthcare Use Cases.
AI in the gaming industry
Games are one of the oldest platforms for AI. Previously, algorithms simply controlled enemies. Now – this is:
- “smart” characters with behavior dependent on player actions;
- dynamic worlds that adapt to the style of passing;
- In-game product recommendation systems.
More details in the material on AI in game development.
Dynamic pricing
Airbnb, Uber, Booking, and other platforms change prices depending on demand, time of day, and competitors. These decisions are not made by a person, but by an agent trained on historical data and the current context.
Retailers also apply such approaches. You can build an agent into an ERP system and adapt prices on the fly without overloading analysts.
Robots in production
In factories, especially in China and Germany, AI agents already operate entire conveyor systems. They are:
- monitor equipment wear;
- Predict breakdowns;
- automatically reconfigure the lines to a different product format.
Advantages: fewer accidents, less scrap, higher accuracy.
Read more: AI in Manufacturing.
Recommendation systems
Netflix, Spotify, YouTube, TikTok – not people, but agents, are behind the selection of content. And not just based on “I watched it – I like it”, but taking into account the pace of viewing, pauses, rewinds.
Businesses can use similar technologies to recommend goods, video tutorials, vacancies, and services. It shortens the customer’s path to purchase.
Agent systems in e-commerce
On the websites of retailers, agents “look” at the user’s behavior: what he is looking for, where he lingers, and how he moves his mouse. Based on this:
- Select the relevant articles
- Suggest what to take in the kit..
Details – in Generative AI in E-commerce.
Contact us and let’s power your project with AI!
Challenges in implementing AI agents
Implementation of AI agents is rarely rapid. Even if you have an idea, budgets, and a team, dozens of “little things” can arise that slow down the process. Usually, these “little things” become the reasons why companies never reach their goals.
- Lack of a clear application scenario.
AI doesn’t work “just like that.” To start an agent, you need to clearly understand what task it will solve. For example, automate customer responses? Reduce the burden on operators? Increase conversion on the site? Without that clarity, the result will be fortuitous – and often disappointing.
- Lack of data or poor quality.
AI agents learn from data. But in companies, data is often scattered, outdated, or simply unavailable. For example, CRM is not synchronized with the site, and user cases are stored in email chains. As a result, the model is “blind” and cannot work correctly.
- Integration with existing systems.
The AI agent must fit into the infrastructure. Examples of AI agents include applications to APIs, security, and access to internal data. Without the participation of technical specialists on the business side, the project can stop at the stage of approvals.
- Lack of competencies within the company.
Even if you have an IT department, this does not mean that it knows how to work with ML or NLP. Implementing AI requires a team that understands how models work, can learn and scale them. This is where external contractors come to the rescue – for example, we at Data Science UA.
- High expectations for the first version.
Many companies think that an agent example will immediately give the perfect result. But the reality is this: the first version is always a test one. Its task is to show direction, not to replace the department. Only through iterations is a stable effect achieved.
Future trends for AI agents
What we see now is just the beginning. AI agents from the experiment go into the category of working infrastructure. Here’s what businesses should consider now.
Models will be smaller but smarter.
Previously, they relied on scale: GPT, Claude, Gemini. Now the emphasis is shifting to highly specialized models trained on their data. This makes the agent cheaper, faster, and safer – after all, he does not “chat too much”.
There will be a turnkey agent market.
As at one time, site designers and CRM systems appeared, so did AI agents. There are already platforms where you can build an agent without code and embed it into the product. It lowers the entry threshold for small and medium-sized businesses.
AI will become part of the “invisible infrastructure”.
Just as no one thinks about how a search engine or mail filter works, so agents will be invisible to users. They will simply work in CRM, in support, in logistics, without requiring attention, but increasing efficiency.
5 easy steps to get started with AI agents for your business
The implementation of AI agents should not begin with the choice of technology or model. Everything is simpler and more pragmatic.
Step 1. State the problem.
Instead of “adding AI”, determine where you have a gap. For example, customers often cannot get a response at night. Or managers spend hours sorting through applications. This is the starting point.
Step 2. Evaluate the data.
Do you have historical information that can help the model “understand” your task? For example, chat logs, email correspondence, and order history. If there is no data, the agent will not be able to work.
Step 3. Select an agent format.
This can be a chatbot, an internal assistant, a voice agent, or a script in CRM. It is important to choose a tool that will not interfere with the usual process, but, on the contrary, will be built into it.
Step 4. Find a professional team
Your task is to solve business problems. Working with data, training models, and setting up integrations is the responsibility of the AI team. The team must understand real business problems.
Step 5. Test, improve, scale.
You need to run MVP, collect feedback, and make edits. It is according to this scheme that all successful projects work – from Amazon to local online stores.
So, is AI a trend or a must-have?
AI agents are not a fashion or a game of the “future”. This is a practical tool for improving business efficiency today. Companies that manage to adapt gain an advantage: respond faster to customer requests, reduce costs, and are less dependent on hiring.
The question is not “whether to use an AI agent”. The question is what task you want to solve. At Data Science UA, this is how we work: assisting businesses in choosing what really works.
FAQ
What are some popular real-world examples of AI agents today?
- Bank of America, HSBC, and Revolut chatbots process many customer requests, help recover a password, check a balance, or open a deposit.
- GitHub Copilot – helps developers write code faster by offering ready-made blocks and patches in real time.
- AI agents in delivery services – in Glovo, Uber Eats, and other platforms agents coordinate couriers, determine optimal routes, and predict arrival times.
- Internal assistants in large companies – Salesforce, SAP, Microsoft – implement agents that help managers find the information they need, prepare reports, and interact with customers.
What role do AI agents play in enhancing customer support?
- Answer typical questions – delivery, return, prices, availability of goods.
- They sort appeals – the hard task goes to the worker, the rest are processed automatically.
- They learn from previous appeals – over time, they become more accurate and useful.
- Increase customer satisfaction, because the response time is reduced by 5-10 times.
What industries benefit the most from AI agents?
- eCommerce – order processing, support, recommendations.
- Banking sector and fintech – verification, support, chatbots, financial assistants.
- Logistics and delivery – routes, schedules, communication with customers.
- Medicine – assistance to doctors in documentation, assistants for patients, support for call centers.
- Real estate – work with applications, evaluation of objects, and customer support.
- Education and EdTech are interactive assistants for students, and automation of communication with users.
But the industry is not the main thing. If a company has a task that can be formalized and automated, most likely an AI agent can handle it.






